© National Safe Skies Alliance - Authored by InterVISTAS Consulting



CBP Airport Technical Design Standard

Finding 10: Use Phased FIS Capacity Approach with
Growth Triggers
One of the greatest sources of confusion with the Airport Technical Design Standards is the set of tables used to calculate baseline space allocation. In the 2016 update to the ATDS, CBP has indicated that there is: a) flexibility to the baseline space requirements; and b) a process through the CBP Field Operations Facilities Program Management Office Project Manager (FOF PMO PM) to allow exemptions from the ATDS.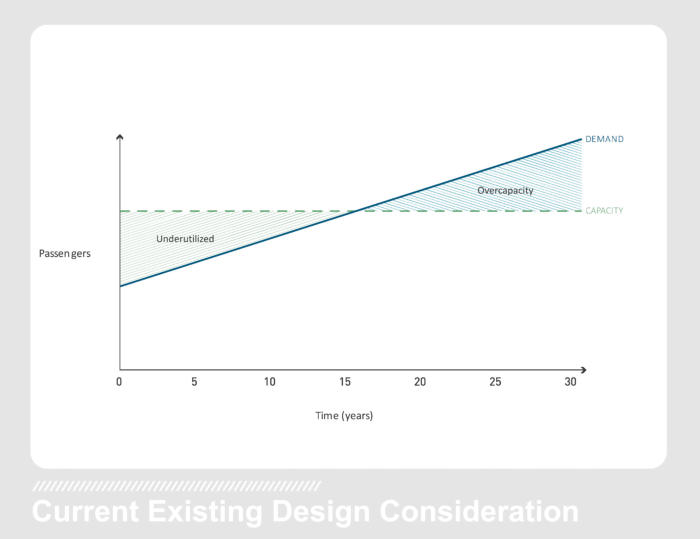
Airport Applicability
- Small to medium passenger volumes - All airport types - All passengers typesReferences
ATDS (2012) - Section 2.7.4 states that the FIS must accommodate all arriving passengers and queues at peak times - Section 3.1 introduces the airport size specification ATDS (2016 - 90% Draft) - Section 2.7 states that the FIS size is determined by passengers arriving at peak hours plus the size of aircraft which arrive - Section 5.3 outlines the space matrix and calculations required for the FIS - Code ATD-01-03 in Chapter 5

Finding 10: Use A Phased FIS Capacity Approach with
Growth Triggers
In the ATDS, the set of tables used to calculate baseline space allocation has caused some confusion. In the 2016 update to the ATDS, CBP has indicated that there is: a) Flexibility to the baseline space requirements b) A process through the CBP Field Operations Facilities Program Management Office Project Manager to allow exemptions from the ATDS.


© National Safe Skies Alliance
Authored by InterVISTAS Consulting

CBP Airport Technical Design Standard
Finding 10: Use Phased FIS
Capacity with Triggers
One of the greatest sources of confusion with the Airport Technical Design Standards is the set of tables used to calculate baseline space allocation. In the 2016 update to the ATDS, CBP has indicated that there is: a) flexibility to the baseline space requirements; and b) a process through the CBP Field Operations Facilities Program Management Office Project Manager (FOF PMO PM) to allow exemptions from the ATDS.
Delivery of facilities could be done with
shell space as quickly as one year, or
for larger projects 2-3 years. The
amount of flexible space could ensure
that the timing of capital and
operations are not out-of-sync and
meet demand appropriately.
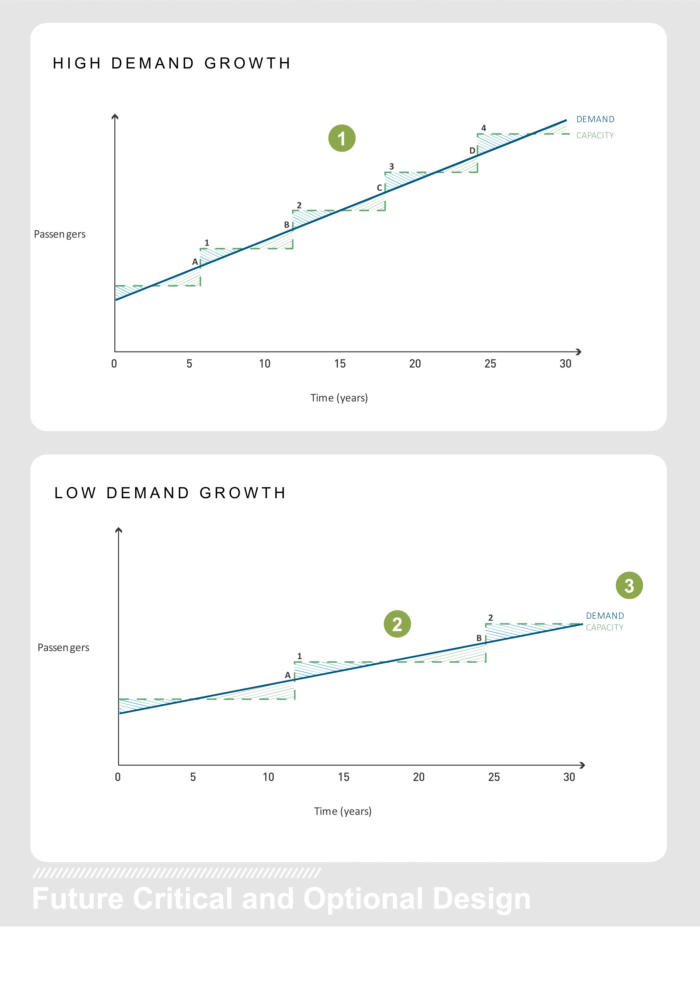
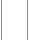
For example after approximately 12
years within an existing facility, demand
growth may be slower than anticipated.
Phased capacity expansion may be built
to accommodate the increased number
of passengers up until a trigger point is
reached. The airport may then proceed
to execute construction for phase 2
capacity expansion in order to meet
demand only when and if it is needed.
The series of triggers and phases
provides flexibility for an airport to
expand when growth warrants it, not be
fixed calendar dates. All of this should
be tied to both the physical processing
capacity (passengers per hour) from a
spatial and processor (e.g. kiosk, other
automation) solution.